Nourishing Minds: The Role of Healthy Diets in Mental Health

Nourishing Minds: The Role of Healthy Diets in Mental Health
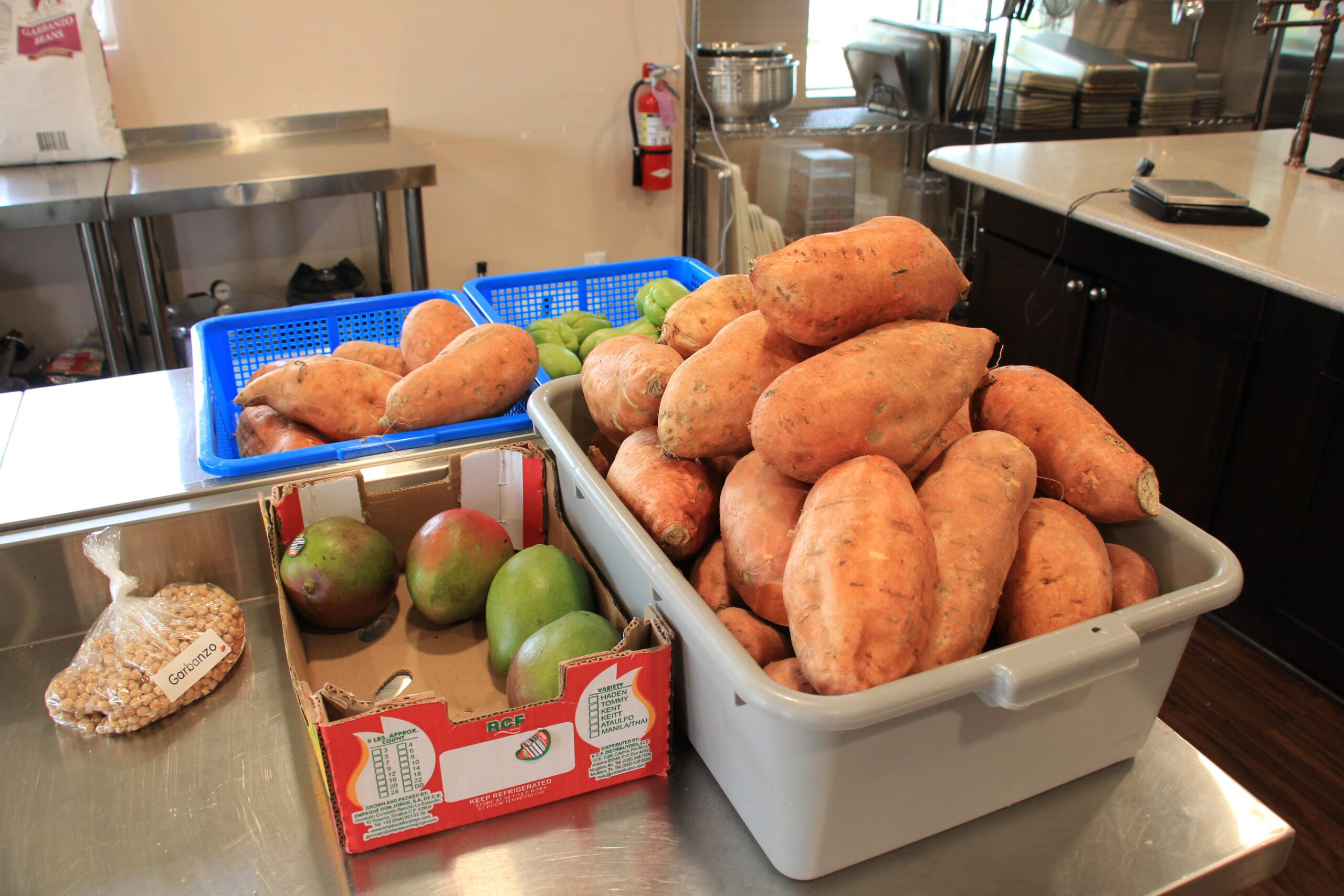
May was Mental Health Awareness Month, a time dedicated to raising awareness about mental health issues and promoting the importance of mental well-being. One often overlooked aspect of mental health is the significant role that diet plays in our mental and emotional well-being. Just as our bodies required nutritious food for physical health, our brains needed a balanced diet to function optimally. At Advance, we made it a point to include and utilize nutrient-dense foods in the meals we served to our community and in the Nutrition Boxes given to our participants. Let’s explore how healthy diets contributed to better mental health and provide practical tips for incorporating brain-boosting foods into your daily routine.
The Gut-Brain Connection
The connection between our gut and brain is powerful, often called the “gut-brain axis.” This bidirectional communication system meant that the health of our gut could significantly impact our mental state. A diet high in processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats could lead to inflammation, which has been linked to mental health issues such as depression and anxiety.
Conversely, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats supported a healthy gut microbiome. This, in turn, could improve mood and cognitive function. For instance, omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish like salmon and trout, were known to reduce inflammation and have been associated with lower levels of depression.
Nutrients for Mental Health
Certain nutrients played critical roles in brain health and function. Here are some essential nutrients and their mental health benefits:
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: As mentioned, these were essential for brain health. Studies showed that omega-3s could help reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety.
- B Vitamins: B6, B12, and folate were crucial for producing brain chemicals that affected mood and other brain functions. Deficiencies in these vitamins were linked to an increased risk of depression.
- Vitamin D: Often referred to as the “sunshine vitamin,” vitamin D was essential for brain health. Low levels of vitamin D had been associated with a higher risk of mood disorders, including depression.
- Antioxidants: Vitamins C and E, found in fruits and vegetables, helped protect the brain from oxidative stress, which could damage brain cells and contribute to mental health disorders.
- Magnesium: This mineral helped regulate neurotransmitters, which sent messages throughout the brain and body. Low magnesium levels were linked to a higher risk of depression.
Foods to Boost Mental Health
Incorporating a variety of nutrient-dense foods into your diet could significantly benefit your mental health. Here are some top picks:
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, and sardines were excellent sources of omega-3 fatty acids.
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and other leafy greens were rich in folate and other essential nutrients.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds provided healthy fats, antioxidants, and magnesium.
- Berries: Blueberries, strawberries, and blackberries were high in antioxidants that protected the brain.
- Whole Grains: Oats, quinoa, and brown rice could help stabilize blood sugar levels and provide steady energy for brain function.
- Probiotic-Rich Foods: Yogurt, kefir, and fermented foods like kimchi and sauerkraut supported a healthy gut microbiome, which in turn benefited mental health.
Practical Tips for a Brain-Healthy Diet
- Plan Balanced Meals: Aim for meals that included a variety of nutrients. A balanced plate might have consisted of a portion of fatty fish, a side of leafy greens, a serving of whole grains, and a handful of nuts.
- Stay Hydrated: Dehydration could affect mood and cognitive function, so drinking plenty of water throughout the day was essential.
- Limit Processed Foods: Reducing your intake of processed snacks, sugary drinks, and fast food, which could contribute to inflammation and negatively impact mental health.
- Mindful Eating: Paying attention to what you ate and how it made you feel could help you make better food choices that supported your mental well-being.
- Seek Professional Advice: If you were struggling with your diet or mental health, considering consulting with a nutritionist or mental health professional who could provide personalized guidance.
Conclusion
Healthy eating was a powerful tool for enhancing mental health. By understanding the connection between diet and mental well-being, we could make more informed food choices that supported both our physical and mental health. This Mental Health Awareness Month, we committed to nourishing our minds with the same care and attention we gave our bodies. After all, a healthy mind started with a healthy diet.
Additional Resources
For more information on mental health and nutrition, check out these resources:
Remember, taking small steps towards a healthier diet could lead to significant improvements in your mental health. Start today and feel the difference!